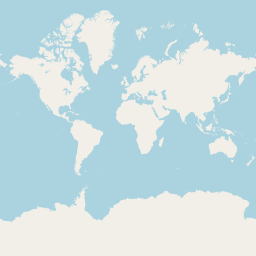
Mercator Projection
The most commonly used projection is the mercator projection.
Projections are used on the mapdata to translate coordinates to pixelpositions. There are various projections that can be used. All implemented ones are showcased here.
The most commonly used projection is the mercator projection.

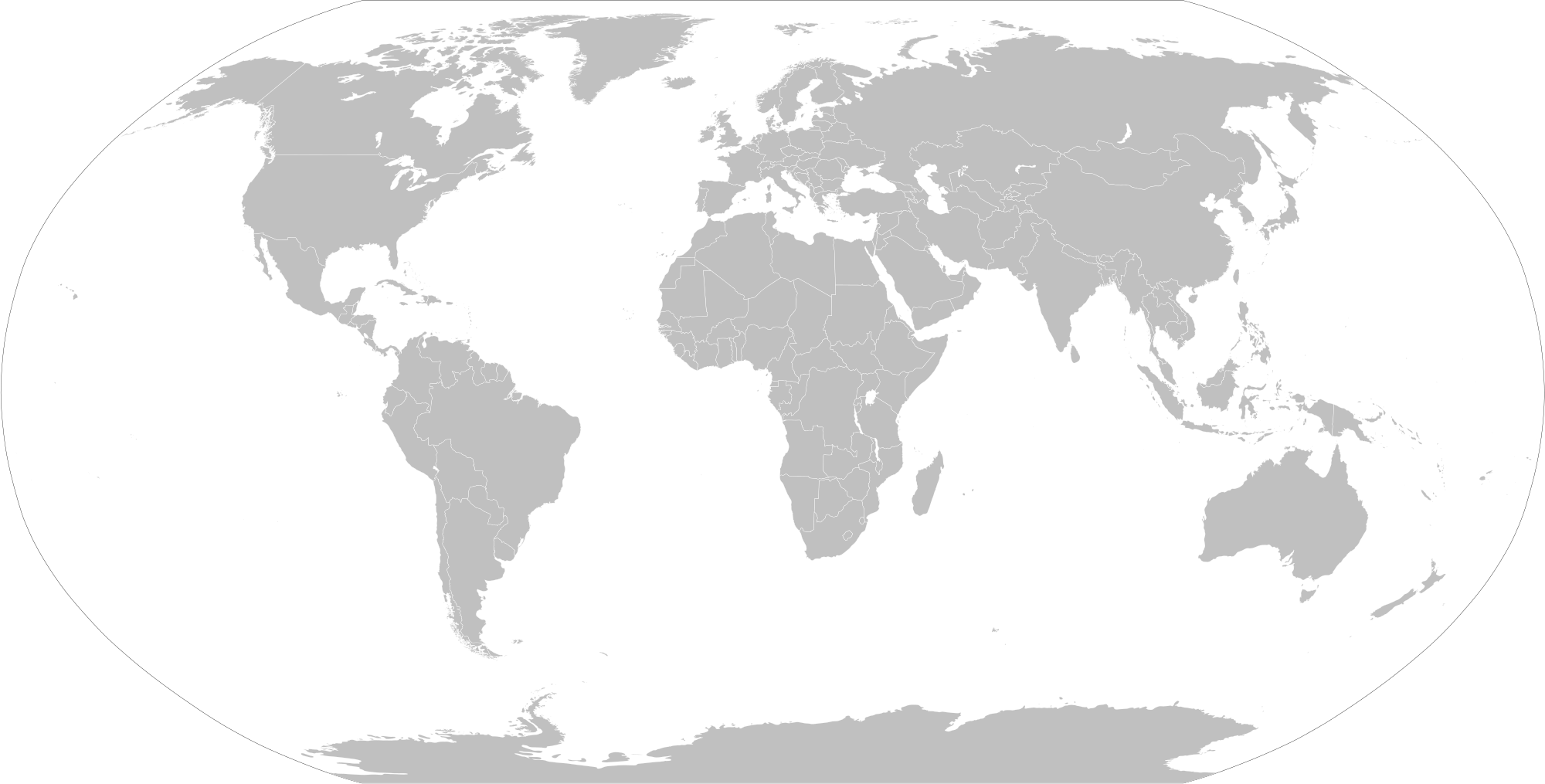
The robinson projection is a more 'artistic' approach, as it follows a table instead of a strict formula. It has severe distortions at the poles, but that distortion declines rapidly heading towards the equator.